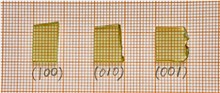
High quality single crystals of Tm,Ho:GdScO3 were grown using the Czochralski method. The transmittance spectra of (100), (010) and (001) planes of the crystal were measured at room temperature, and the absorption coefficient and absorption cross-section of the crystal were calculated. The transition intensity parameters Ωtfor Tm3+ and Ho3+ co-doped crystal were fitted using the product of dopant concentration N and absorption oscillator intensity f was fitted as a parameter, and the spectral parameters such as spontaneous radiation transition probability, radiative lifetime and fluorescence branching ratio were also calculated. The results show that, the Tm,Ho:GdScO3 crystal has good luminescence performance, and the calculated spectral parameters provide data reference for the study of its laser output performance.
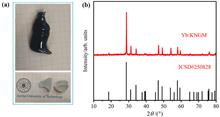
Yb3+ doped (atomic number fraction of 5%) gadolinium-sodium-potassium molybdate laser crystal K0.1Na0.9Gd(MoO4)2 was grown by Czochralski method in this work. Then the crystal structure was characterized and the density, specific heat, thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity were measured. Additionally, a simple and effective theoretical fitting method for specific heat and thermal diffusivity was proposed, and the fitting results were in good agreement with the experimental results. The results have shown that, the crystal belongs to tetragonal crystal system, with the structural characteristics of scheelite, the experimental density and theoretical density are 5.3792 g/cm3 and 5.3460 g/cm3, respectively, the Vickers hardness of the crystal along the b-axis is 251.5 kg/mm2, and as the temperature increases, the thermal conductivity of the crystal decreases from 1.03 W⋅m-1⋅K-1 at 300 K to 0.91 W⋅m-1⋅K-1 at 400 K. The specific heat of the crystal at 300 K is about 0.62 J·g-1·K-1, indicating that the crystal has a high thermal damage threshold. Under the excitation of InGaAs laser diode with the wavelength of 970 nm, the strongest emission peak of the crystal appears at 1023 nm with bandwidth of 43 nm, indicating that the crystal is promising for broadband tunable and ultrashort pulse laser. The study of the mechanical, thermodynamic, and spectral properties of the crystal can provide an important reference for the study of its laser performance.
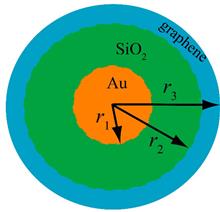
To study the scattering properties of core-shell structure containing graphene, expecially electric field distribution, energy density, and radiative/nonradiative decay rate properties, the transfer matrix method (TMM) is used to evaluate the effects of wavelength of the incident ray and dipole emitter location on the spontaneous radiation of Au@SiO2@Graphene. It is found that when the core size and shell thickness remain constant, the Purcell factor in the near-field region of the core-shell structure increases with the increase of the thickness of the intermediate SiO2 dielectric layer. And the Purcell factor of the core-shell structure decreases with the distance of the dipole emitter from the center of the sphere, realizing the regulation of spontaneous radiation. On the other hand, by optimizing the structural parameters of graphene-based core-shell structure, the maximum value of the Purcell factor in the visible light range is achieved at about 633 nm. When the thickness of the dielectric layer is fixed, increasing the radius of the model will lead to a decrease of the Purcell factor. And changing the size parameters of the model can effectively strengthen the interaction between the graphene-based core-shell structure with light wave. The research can provide a reference for the solar thermal field.
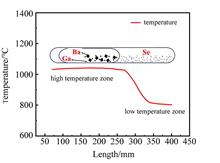
BaGa4Se7 (BGSe) is currently attracting considerable attention as a new type of infrared nonlinear crystal. We explored the synthesis of BGSe polycrystalline raw materials using both the two-temperature zone method and the high-pressure-assisted method, and designed a rapid purification method with a large temperature gradient to purify the synthesized polycrystalline material firstly. And then, the phase composition and impurity concentration of BGSe polycrystals before and after purification were characterized using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The X-ray diffraction spectra are consistent with theoretical simulation results, showing no impurity peaks. ICP-MS test results also show a significant reduction in the content of metal impurities such as Fe, Al, and O impurity in the ingot after purification. The research can provide a raw material basis for the growth of high-quality single crystal.
In order to obtain the tellurite glass with good thermal stability and high-intensity luminescence, WO3 is doped into the TeO2-ZnO-Na2O system to improve the anti-devitrification and thermal stability of the glass. The results show that the ΔT of the tellurite glass increases from 110 °C without WO3 to 142 °C with WO3 content of 20 mol%. On the basis of thermal stability study of tellurite glass, the spectral properties of single-doped Er3+ and Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped tellurium tungstate glasses are further studied. The research results show that under the co-doping conditions of Er3+/Yb3+, the energy transfer between Er3+/Yb3+ improves the absorption efficiency of Er3+ ions for 980 nm pump light, and the luminescence intensity in the 1.5 μm band is enhanced. Finally, Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped tellurium- tungstic glass with high-intensity 1.5 μm band emission is obtained, indicating that the co-doping of Er3+/Yb3+ is an effective method to achieve high-intensity luminescence in the 1.5 μm band.